Case of Juman Mountain Forest Fire in 2017
(2019)
QHow much did the amount or the concentration of Cs released to river water by forest fire? How did them change by time?
AThe release rate of radioactive cesium was higher in the burned area than that previously observed. It is assumeed that the release rate becomes same level of the unburned area with the plant coverage recovering in burned area.
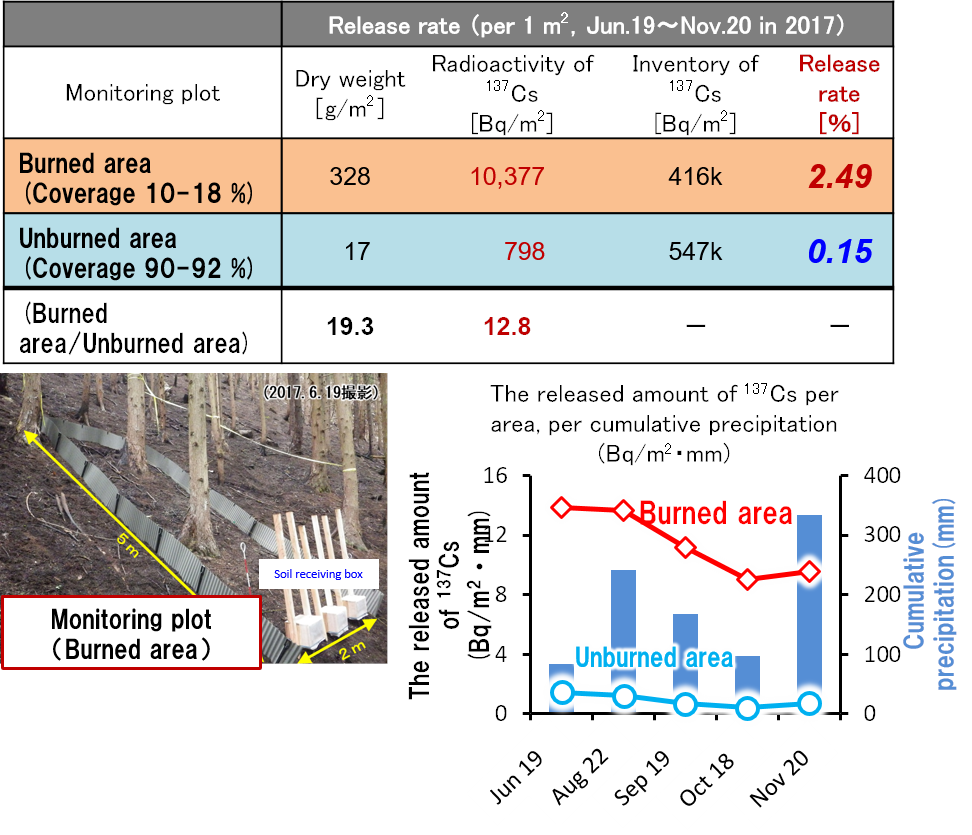
- JAEA has observed the release of radioactive cesium about a half year from 1 month after the extinguishment.
- In the result of the monitoring, the release rate of radioactive cesium was higher in the burned area than that previously observed because the plant coverage decreased in the burned area.
- For the reason above, it is considered that the release rate becomes same level of the unburned area with the plant coverage recovering in burned area.
Table 1 Other data of the release observation
| Place | Vegetation | Release rate (covorage) |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper area of Uda river | Japanese red pine, ceder, broad-leaved trees, Japanese cypress | 0.086~1.1% (Coverage 5~95%) |
錦織 et al., 2015 |
| Kawamata Town | Japanese ceder | 0.07% (Coverage 95%) |
Yoshimura et al., 2015 |
| Broad-leaved trees | 0.05~0.12% (Coverage 86~99%) |
Niizato et al.,2016 | |
| Broad-leaved trees (decontaminated) | 0.84% (Coverage 30~50%) |
渡辺et al., 2019 |
Related articles
- Does the concentration in river water change before and after forest fire? How did it change by time?
- Any method to evaluate damaged location by the forest fire?
- Do sediment with high radioactive cesium concentration continue to be deposited on river bottoms?
- Is there a continuous input of cesium contamination to rivers from forests?
- When it rains, does radioactive cesium flow out of forests with soil? 【137Cs flow from river basins and mountain slope】
