Effects on Ecosystem
(2016)
QIs there any increase in the number of mutations caused by radiation among wildlife in Fukushima prefecture?
ANational Institute for Environmental Studies developed a plant and cultured cells in which the scars in DNA caused by radiation can be observed. Experiments using these cultured cells showed that no concern is warranted regarding increased mutations in wildlife DNA in 99.5% of the difficult-to-return zones as of October 2016.
- Organisms have a mechanism to repair damaged DNA. Mutation appears when balance is lost between the amounts of DNA damage and DNA repair.
- Double-strand damage caused by radiation is repaired through homologous recombination repair (Fig.1).
- We investigated the balance between the amounts of DNA damage and repair using cultured cells derived from this plant to find that the amount of repair outpaced damage at 16 µSv/h (Fig. 3). This means that no increase in wildlife DNA mutation occurred in 99.5% of difficult-to-return zones (Fig.4).
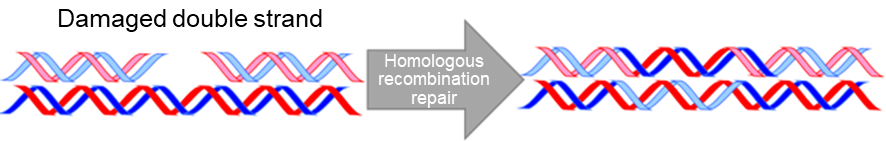
Fig.1 Double-strand damage and homologous recombination repair
DNA with double strand damage is repaired utilizing homologous DNA (DNA having the same or a similar sequence).
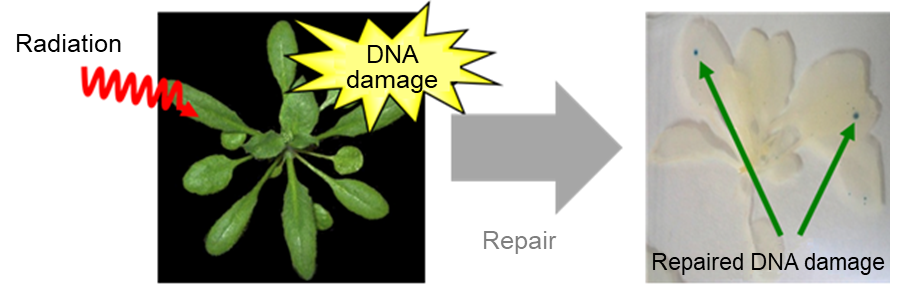
Fig.2 Plant in which repaired DNA damage can be observed
Cells in which DNA double-strand damage occurred and were then repaired, as indicated by the cells having produced a color.
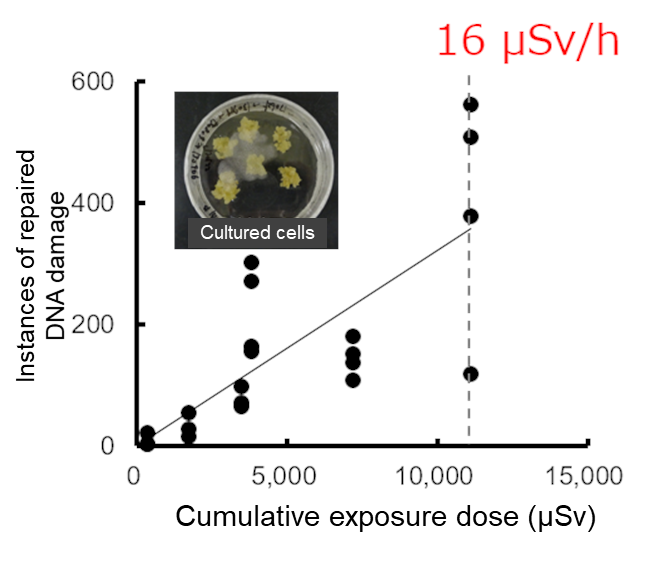
Fig.3 Relation between exposure dose and repaired DNA damage
This figure shows that, with an exposure dose up to approximately 16 µSv/h, the amount of DNA repair increased in accordance with the exposure dose, and an increased amount of DNA damage was also repaired in accordance with the exposure dose (i.e., the amount of repair outpaced the amount of damage).
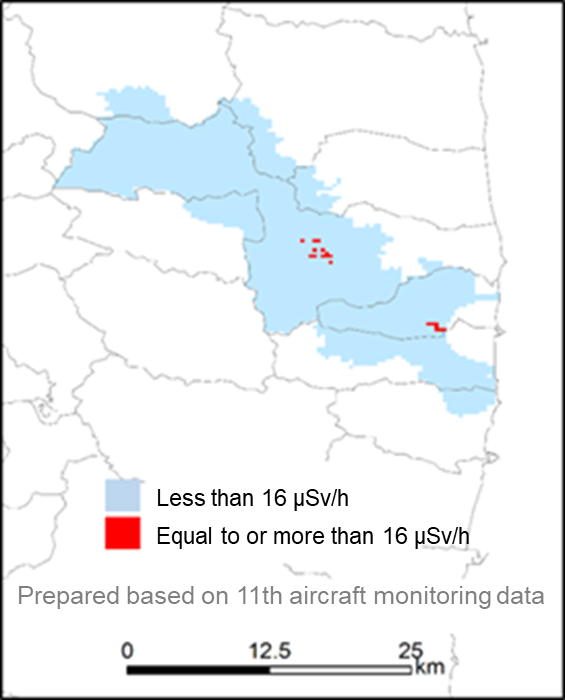
Fig.4 Map of mutation accumulation risk as of November 2016
Wildlife DNA mutation is not likely to occur in 99.5% of the zones.
Note: Although the efficiency of DNA repair has not been investigated for all organisms, it can be considered that there is no significant difference in the DNA repair mechanism, which provides the basis of all life support.
Related articles
- How have ecosystems changed in evacuation-order zones?
- What is the current concentration of radioactive cesium in edible wild plants in Fukushima Prefecture?
- I heard most of the forests would not be decontaminated. Does cesium remain in the forests?
- Does the concentration of radioactive cesium deposited in mountain forests vary by altitude and location?
- Is there a continuous input of cesium contamination to rivers from forests?
