Radioactivity Dynamics in River System
(2015)
QWill the concentration of radioactive cesium in lake water remain high unless contaminated sediments are removed from reservoir beds? 【Tendency of the change of the concentration in reservoir beds】
AInvestigations at the Mano dam (Hayama lake) in Fukushima Prefecture have revealed that most of the radioactive cesium flowing into the dam is deposited into the bottom sediment. Nevertheless, the concentration of radioactive cesium in the lake water does not increase.
Fig.1 Sampling spots at Hayama lake (Mano dam)
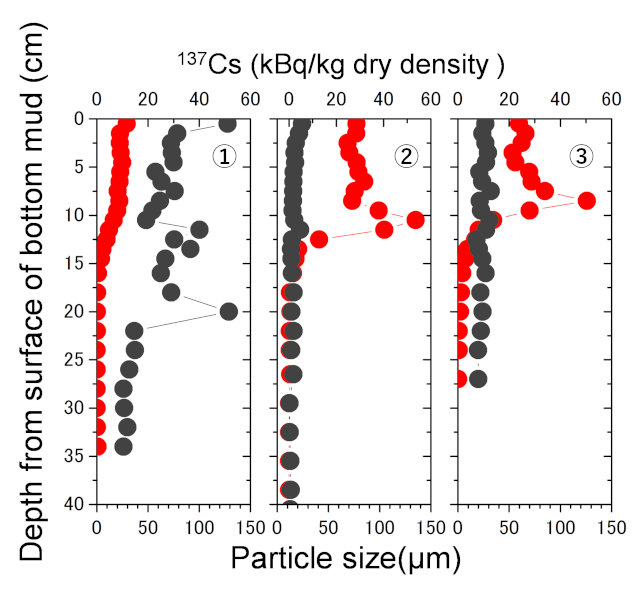
Fig.2 Vertical depth distribution of 137Cs and dry density of bottom sediments (Collected in autumn 2014(①, ②), spring 2015(③))
-
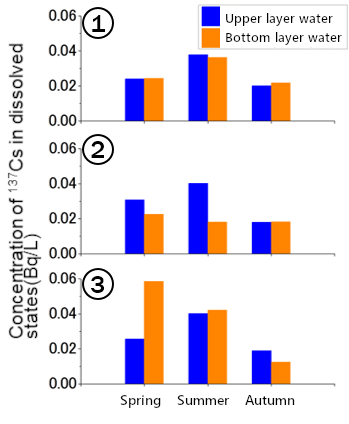
Fig.3 Dissolved state 137Cs concentration of lake surface water and bottom water (collected in 2015)
- In the Mano dam lake, the largest amount of cesium seems to be deposited in the deeper sediments due to the initial accident fallout.
- Now, the cesium concentration in the soil inflow is low. This is deposited on top of the layer with high cesium content.
- Many dams play a role in reducing the migration of cesium from upstream to downstream and re-accumulation.
Related articles
- Will the concentration of radioactive cesium in lake water remain high unless contaminated sediments are removed from reservoir beds? 【Tendency of the change of the concentration in reservoir beds】
- Does the concentration of radioactive cesium increase due to the resuspension of sediments by heavy rains?
- When it rains, does radioactive cesium flow out of forests with soil? 【137Cs flow in heavy rain】
- When it rains, does radioactive cesium flow out of forests with soil? 【137Cs flow from river basins and mountain slope】
- Does the concentration in river water change before and after forest fire? How did it change by time?
