Glossary on
"Radioactivity Dyanamics in Forest"
-Trees and flows-
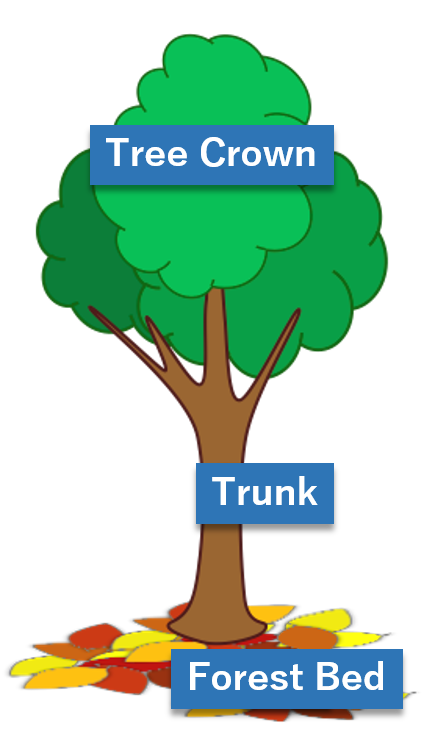
Tree crown
The aboveground part of trees including shafts, branches and leaves.
Trunk
The shaft of a tree. Trunk is the main construction of trees, supporting branches and supported by roots.
Forest bed
Ground surface of forest and nearest part of ground surface.
- Litter layer (L layer)
The layer of depositing raw fallen leaves, branches, barks and fruits. - Fallen leaves layer
The layer aboveground, consisted of fallen leaves, branches and decomposed organic matters. Litter layer contains the litter layer.
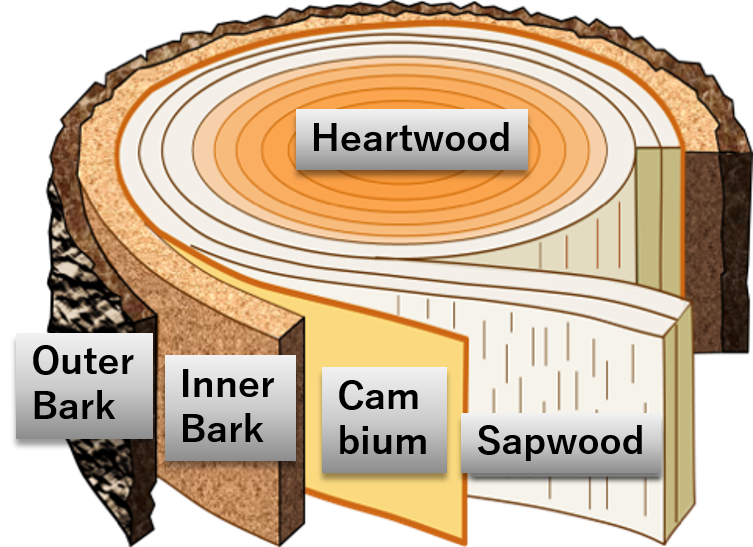
Wood
The wooden part of trees which cut to use as materials.
- Heartwood
The central part of woods. Dark colored, high intensity and durability, and low water content. Heartwood is consisted of dead cells. - Sapwood
The white part of woods around heartwoods. Sapwood is high in amylose and normally high water content, so lower durability than heartwood. Sapwood contains living cells.
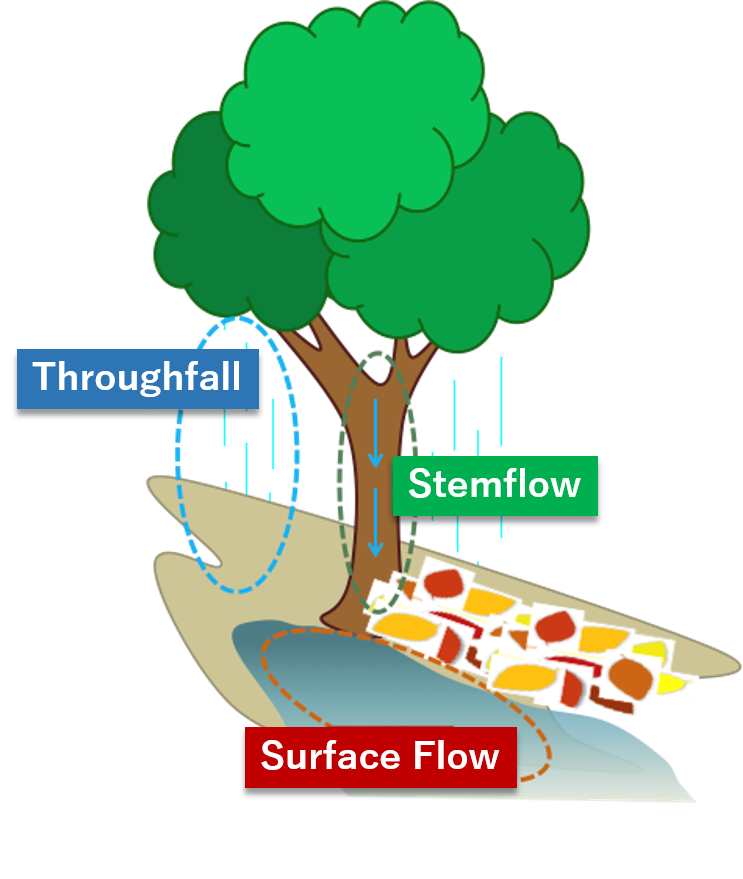
Throughfall
Rainwater falling to forest bed through the crown.
Stem flow
Rainwater flowing along the stems.
Ground water
Water flowing on the ground surface. It contains unpercolated water flowing on the ground or water once percolated and well up again.
Reference
- 森林総合科学用語辞典(東京農大出版会、2015年)
- 樹木学(築地書館、2001年)
- 農林水産省プレスリリース「森林内の放射性物質の分布状況調査結果について」(農林水産省、平成25年3月29日)
