Case of Juman Mountain Forest Fire in 2017
(2017)
QCs released to the environment by the forest fire?
ARelease of radioactive material during Juman-Mtn fire event was limited, and even if existed, the concentration in air is significantly smaller than the usual airborne dust concentration.
- Radio-cesium concentration and levoglucosan (plant combustion index) concentration in the airborne dust were analyzed.
- Levoglucosan concentration indicated high value during the fire event, but low after the event, and it reflected the effect of event.
- On the other hand, definite correlation between radio-cesium concentration and levoglucosan was not observed (highest radio-cesium concentration was found after the fire event)
⇒ Origin of radio-cesium in airborne dust is considered to be other item than the fire.
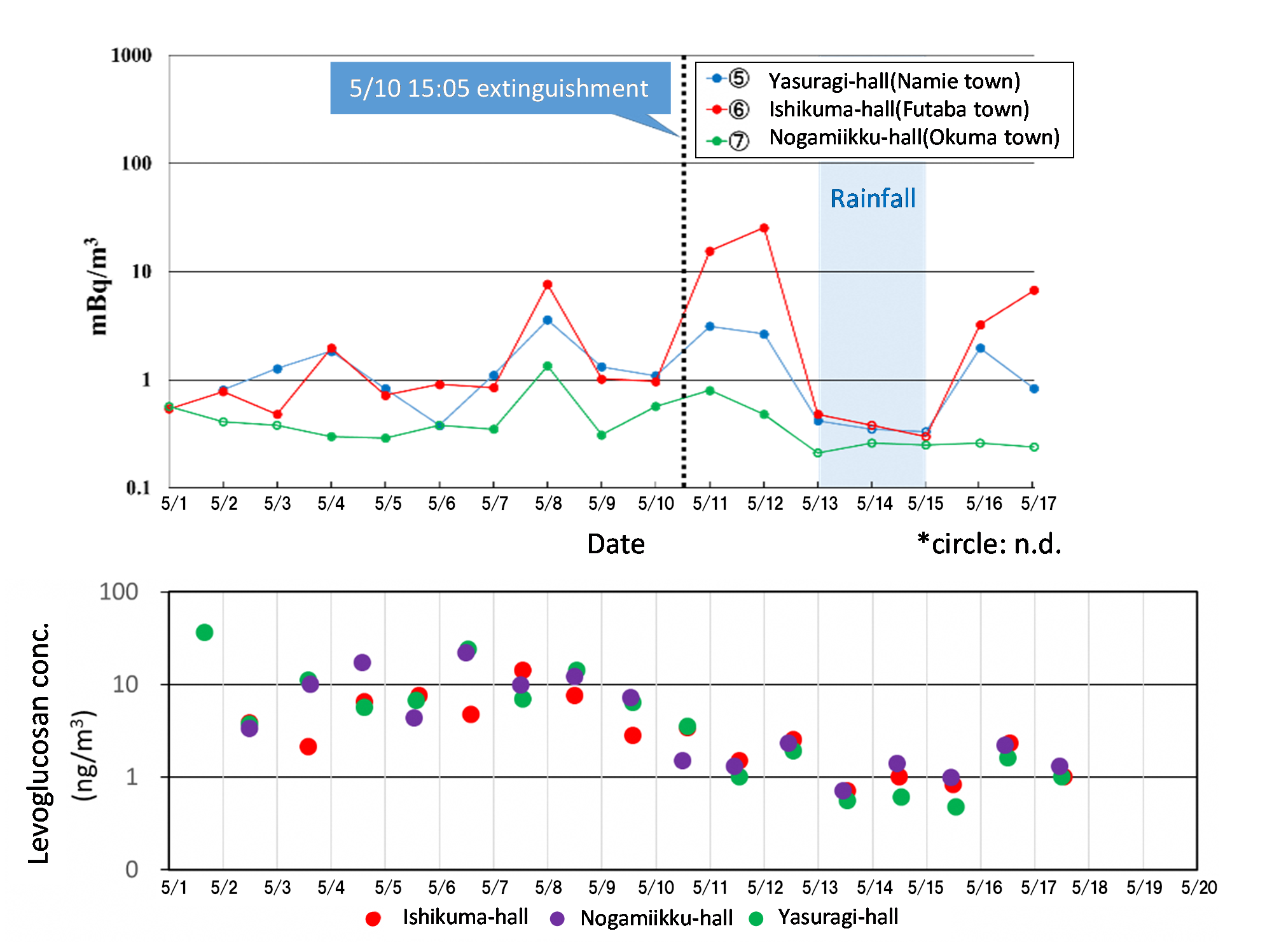
Fig.1 Cs concentration (upper fig.) and levoglucosan concentration (lower fig.) during and after the fire event
Related articles
- What is the source of radio-cesium in the airborne dust sampling?
- How much does additional internal dose exposure would be if we assume highest concentration during the fire event was exposed? How harmful for the health?
- Where were radioactive materials deposited and in what quantities?
- What kinds of radioactive materials were released into the atmosphere and the sea and how much?
- Will clean areas be contaminated due to radioactive cesium flowing out of forests?
