Assessment of Exposure Doses and Decontamination
(2015)
QWhat is the radiation-shielding effect of a house?
AConversion coefficient for reducing radiation is the ratio of air dose rate in house to that of outside. The conversion coefficient of a general house (wooden house, prefabricated house) built in a cesium-deposition area is about 0.4. But the coefficient changes depending on the situation. So the coefficient should be used only as a rough standard.
The reason why air dose rates in houses are lower than those outside
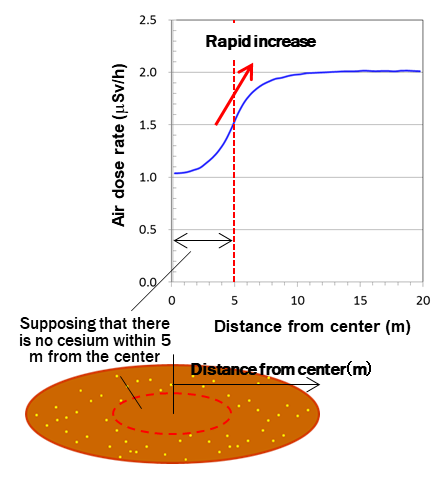
Fig.1 Depandence of air dose rates on the position
(Result from simulation)
- The reason why air dose rates in houses are in general lower is that there is no cesium deposits under the house.
- If there is no radiation source within 5 m from the center, the air dose rate at the center position is about half of that of outside.
- Air dose rate at the border of a house suddenly changes.So air dose rates at the border should be carefully measured.
Conversion coefficients in Fukushima
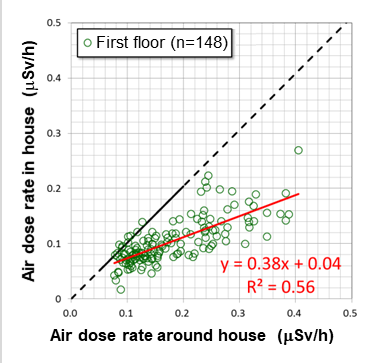
Fig.2 Result for conversion coefficient measured in general houses in Fukushima Prefecture
- Conversion coefficient for reducing radiation at the first floor of a house is about 0.4 on average. But the value changes depending on individual houses.
- In the places where air dose rates are low, the effect of natural radiation from ground should be separately considered.
- We should be careful to measure air dose rates around houses because they change considerably.
(Report on Investigation of Radiation Distribution:
http://fukushima.jaea.go.jp/initiatives/cat03/entry06.html)
Conversion coefficient changes depending on the size and shape of a house.
Related articles
- In what ways does exposure to radiation occur the environment? What kinds of radiation exposures are important in Fukushima?
- Does the radiation dose measured with a personal dosimeter represent the real radiation dose?
- What kinds of measurements and evaluations for radiation doses have been conducted until now? What are the results?
