Assessment of Exposure Doses and Decontamination
(2016)
QWhat kind of unit is used for the evaluation of radiation dose? What is the relationship between the unit and air dose rates?
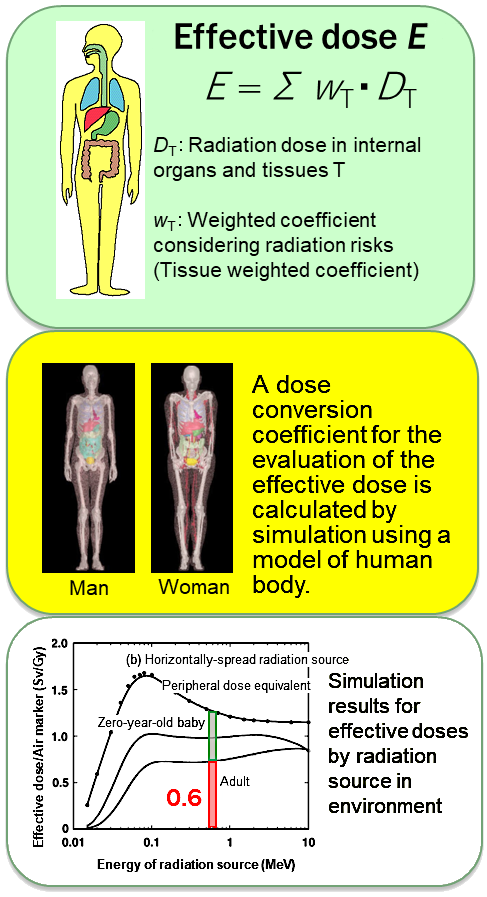
AEffective dose is a unit where the difference in radiation damage risks among internal organs (thyroid gland, lung, etc.) and tissues (red marrow, skin, etc.) are taken into account.
Detailed simulation considering the nature of environmental gamma rays has revealed that a peripheral dose equivalent multiplied by 0.6 corresponds to effective dose for an adult.
- For the evaluation of radiation dose, effective dose E (Sv: Sievert) is widely used.
- Effective dose is a unit where the difference in radiation damage risks among internal organs (thyroid gland, lung, etc.) and tissues (red marrow, skin, etc.) are taken into account.
- Effective dose cannot be measured directly. It is estimated from measurable data using a dose conversion coefficient.
- A dose conversion coefficient is calculated by computer simulation using a model of a human body.
- Peripheral dose equivalent used for the measurement of air dose rate is represented in Sv units. But it should be noted that dose equivalent is different from effective dose E. The value of a peripheral dose equivalent is always larger than the corresponding effective dose.
- In the place where radioactive cesium is deposited on the ground, detailed simulation considering the nature of environmental gamma rays has revealed that a peripheral dose equivalent multiplied by 0.6 corresponds to effective dose for an adult.
(K. Saito et al.: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/
00223131.2014.919885,
D. Satoh et al.: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/
00223131.2015.1021286 )
Related articles
- In what ways does exposure to radiation occur the environment? What kinds of radiation exposures are important in Fukushima?
- Why are radiation doses measured with personal dosimeters different from those estimated using air dose rates?
- Does the radiation dose of a person depend on age, gender, race, and physique?
References
- Saito, K. and Petoussi-Henss, N. (2014): Ambient dose equivalent conversion coefficients for radionuclides exponentially distributed in the ground, Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, vol. 51, no. 10, 1274-1287. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2014.919885
- Satoh, D., Furuta, T., Takahashi, F., Endo, A., Lee, C. and Bolch, W. E. (2016): Age-dependent dose conversion coefficients for external exposure to radioactive cesium in soil, Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, vol. 53, no. 1, 69-81. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2015.1021286
