Radioactivity Dynamics in River System
(2016)
QDoes the concentration of radioactive cesium in river water increase after rainfall? 【Effect of the upstream dam on the 137Cs concentration】
ADuring the periods of high water-level, rivers with a dam in the upstream does not tend to increase the radioactive cesium in the particulate state so much compared to rivers without dams.
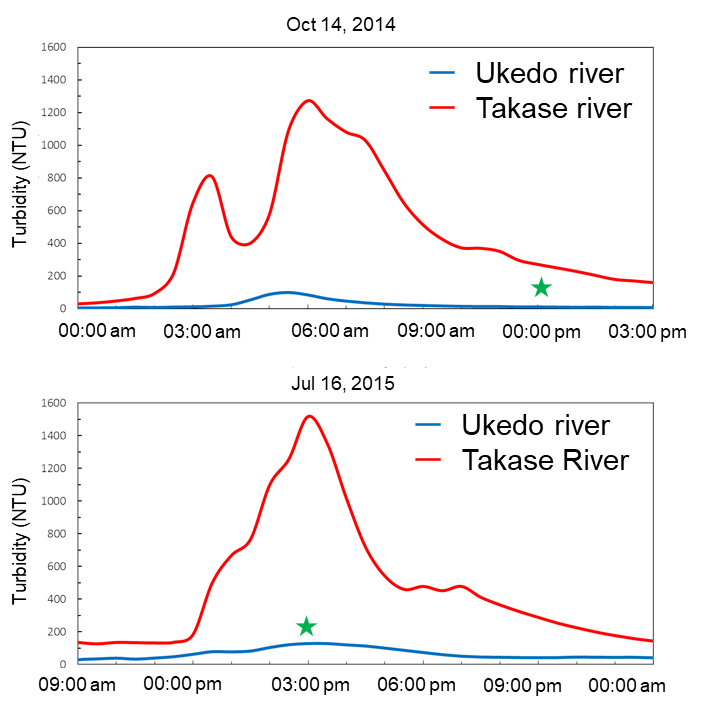
Fig.1 Concentration of suspended materials in river water for the Ukedo River system at the time of high water level
(★: Measurement time in Table 1)
- Investigations of rivers in Fukushima Prefecture have revealed that if there is a dam, sediment discharge from upstream is suppressed even during periods of high water-levels e.g. typhoons. Accordingly, the concentration of radioactive cesium in the particulate state is not so high, because the concentration of suspended materials is low.
- In the Ukedo River (with dam) the concentration of suspended materials in main stream is lower by one order of magnitude than that in the Takase River (tributary of the Ukedo River, without dam upstream). Therefore, even though the concentration of 137Cs in 1 kg of floating suspended materials is high, the 137Cs concentration in the particulate state in the Ukedo River is the same as that in the Takase River.
Table 1 Concentration of floating suspended materials and radioactive cesium in river water at the time of high water level
| Measurement date | Oct 14, 2014 | Jul 16, 2015 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement point | Ukedo river (Ukedo bridge) |
Takase river (Takase bridge) |
Ukedo river (Ukedo bridge) |
Takase river (Takase bridge) |
| Concentration of floating suspended materials (mg/L) | 24 | 233 | 113 | 1,470 |
| Concentration of 137Cs in particulate states per 1 kg floating suspended materials (kBq/kg) | 92 | 9.0 | 65 | 6.8 |
| Concentration of 137Cs in particulate states (Bq/L) | 2.2 | 2.1 | 7.7 | 10 |
Related articles
- Does the concentration of radioactive cesium in river water increase after rainfall? 【Changes of the concentration of 137Cs in heavy rain】
- Do high concentrations of radioactive cesium continue to be deposited on riverbeds? 【Deposition of sediment in riverbeds】
- How does radioactive cesium in forests move from trees to the ground surface? 【Movement in throughfall and stemflow】
- How does radioactive cesium in forests move from trees to the ground surface? 【Movement as particulate and dissolved states】
- How much did the amount or the concentration of Cs released to river water by forest fire? How did them change by time?
