Radioactivity Dynamics in forests
(2020)
QWhere does radioactive cesium absorbed in cedar wood come from?
AA joint research group of the National Institute for Environmental Studies and the Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute investigated cedar forests in Kawauchi Village, Fukushima Prefecture, to find out the source of radioactive cesium absorbed in the wood part of trees with the growth of the trunks.
As a result, they estimated that up to half the amount of radioactive cesium deposited in wood during the five-year period from August 2011 after the accident was absorbed from the soil through the roots. The rest is assumed to be part of the radioactive cesium absorbed from the leaf surface just after the accident, which then moved through the inside of cedar trees.
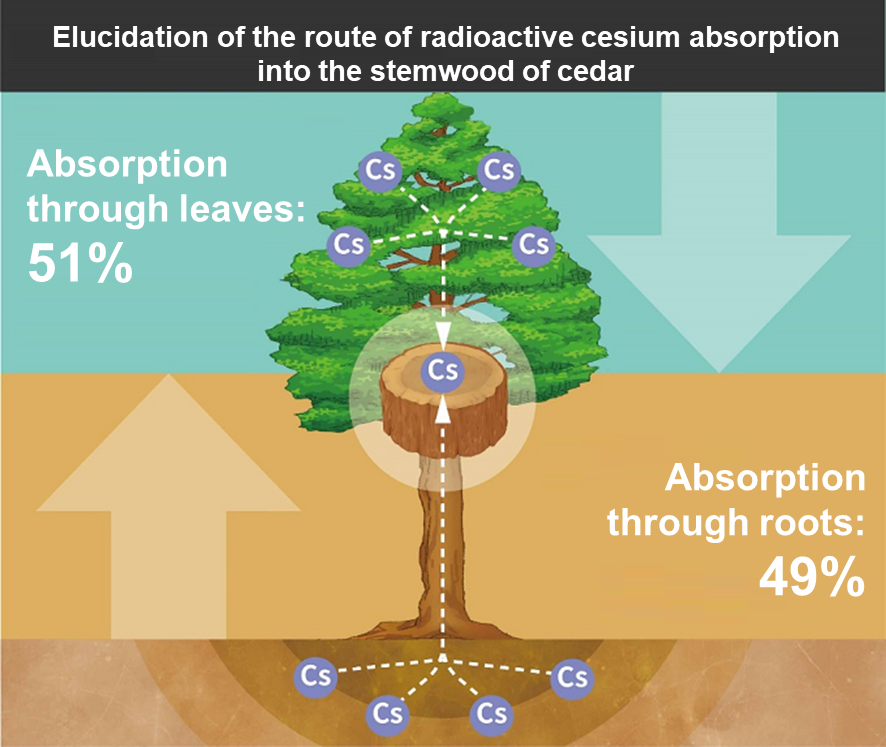
Fig.1 Breakdown of the route of radioactive cesium absorption into the stemwood of cedar
The joint research group of the National Institute for Environmental Studies and the Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute successfully estimated the amount of radioactive cesium absorbed into stemwood through roots by applying a newly invented cesium isotopic approach* to a cedar forest in Kawauchi Village, Fukushima Prefecture, where the radioactive cesium inventory in stemwood is increasing.
In this cedar forest, the radioactive cesium inventory in stemwood increased about 1.3 times in five years from August 2011. The group estimated that up to half the increase over the period was attributable to absorption from the soil through tree roots. The rest is assumed to be part of the radioactive cesium absorbed mainly from the leaf surface just after the accident, which then moved to the stemwood through the inside of cedar trees (see the figure above).
This research has revealed that both absorption through leaves and absorption through roots are important routes of radioactive cesium absorption into the stemwood of cedar.
* Cesium isotopic approach: An approach through which the movement of radioactive cesium is estimated based on the movement of a naturally occurring stable cesium isotope instead of radioactive material.
(Research results from the National Institute for Environmental Studies and the Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute)
Related articles
- I heard most of the forests would not be decontaminated. Does cesium remain in the forests?
- How does radioactive cesium in forests move from trees to the ground surface? 【Movement in throughfall and stemflow】
- How does radioactive cesium in forests move from trees to the ground surface? 【Movement as particulate and dissolved states】
