Radioactivity and Air Dose Rate
(2015)
QHow were the reliabilities of the environmental measurements verified?
AWe verified the reliabilities of the measurements in three ways:
(1) calibrating the measurement instruments using a standard radiation source with a known accurate intensity
(2) obtaining comparative measurements using multiple measurement instruments
(3) having external experts check the obtained results.
◆ Performance verification of KURAMA-Ⅱsystem
The capability of obtaining measurements at the precision specified by the criteria in the JIS standard was verified using a standard radiation source.

Fig.1 Calibration system with a standard radiation source
-
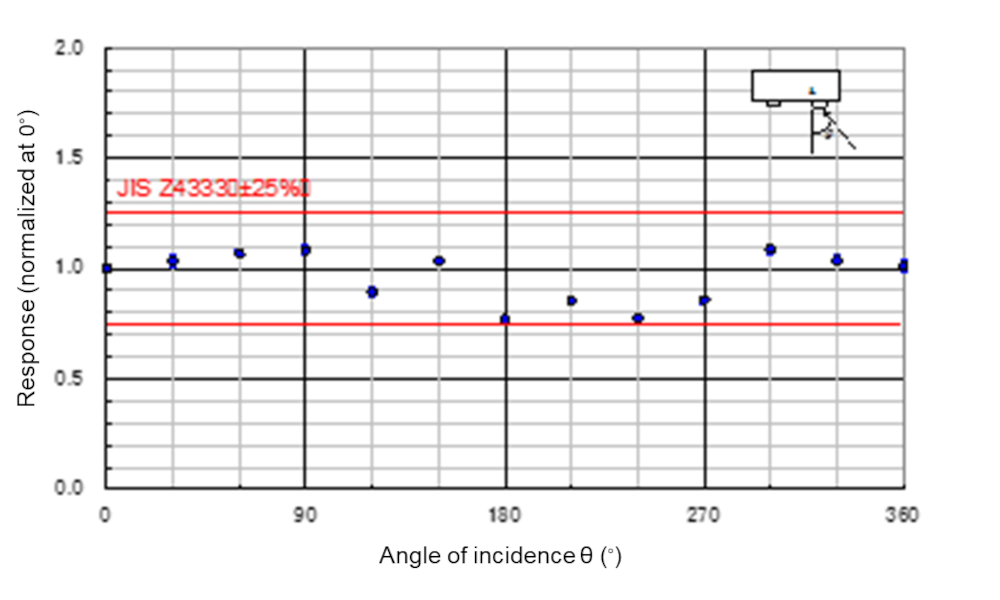
Fig.2 Fluctuations of measured values by direction of incidence
-
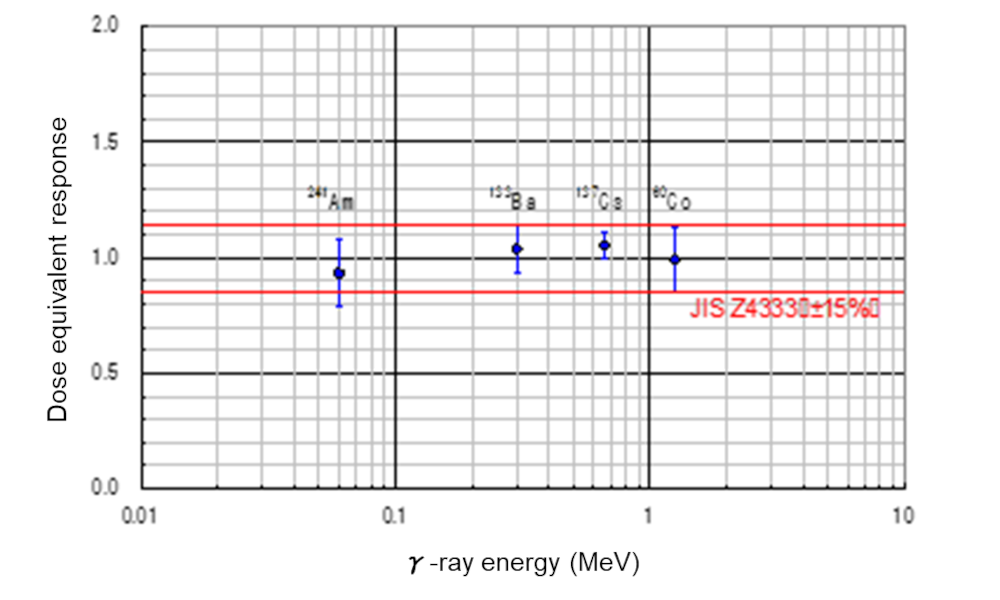
Fig.3 Fluctuations of measured values by energy
(Tsuda et al, 139: 260-265 (2015))
In addition to checking the measurement systems and methods by calibrating and comparing the measurement instruments, the validity of the measurement results was verified by a committee of external experts.
◆ Comparison of in situ measurements using a portable Ge semiconductor detector
-

Fig.4 Scene showing comparison of results
-
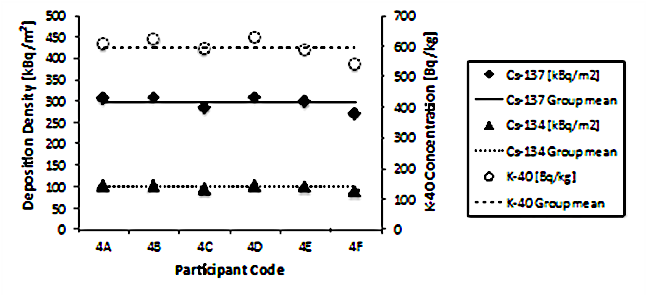
Fig.5 Results of comparison
Similar inventory values were checked to ensure that they had been measured at the same position.
(Mikami et al., Jpn J Health Phys, 50: 182-188 (2015))
◆ Comparison of soil sample measurements using a stationary Ge semiconductor detector
-

Fig.6 Scene showing sample comparison
-
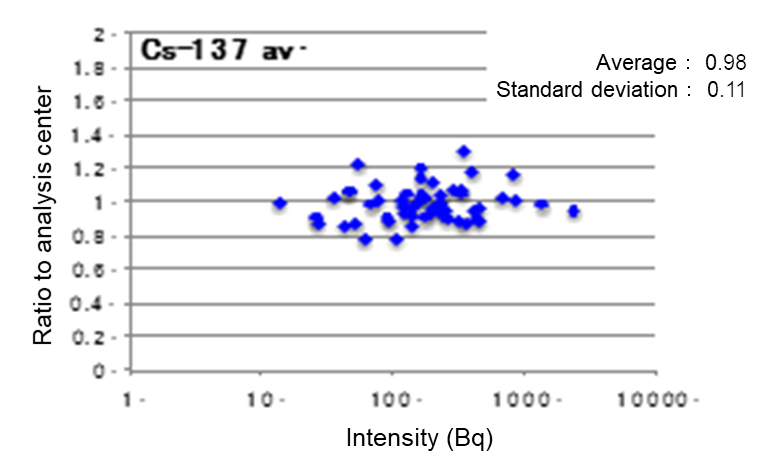
Fig.7 Results of comparison
Similar nuclide concentration values were checked to ensure that they had been measured on a common sample.
(Report on Preparation of Distribution Map of Radiation Doses, etc. (Part 1))
Related articles
References
- Tsuda, S., Yoshida, T., Tsutsumi, M. and Saito, K. (2015): Characteristics and verification of a car-borne system for dose rate in air: KURAMA-II, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, vol. 139, 260-265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.02.028
- Mikami, S., Sato, S., Hoshide, Y., Sakamoto, R., Okuda, N. and Saito, K. (2015): In situ gamma spectrometry intercomparison in Fukushima, Japan, Japanese Journal of Health Physics, vol. 50, no. 3, 182-188. https://doi.org/10.5453/jhps.50.182
