Characteristics of the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES)
The INES Scale is a worldwide tool for communicating to the public in a consistent way the safety significance of nuclear and radiological events. It explains the significance of events from a range of activities, including industrial and medical use of radiation sources, operations at nuclear facilities and transport of radioactive material.
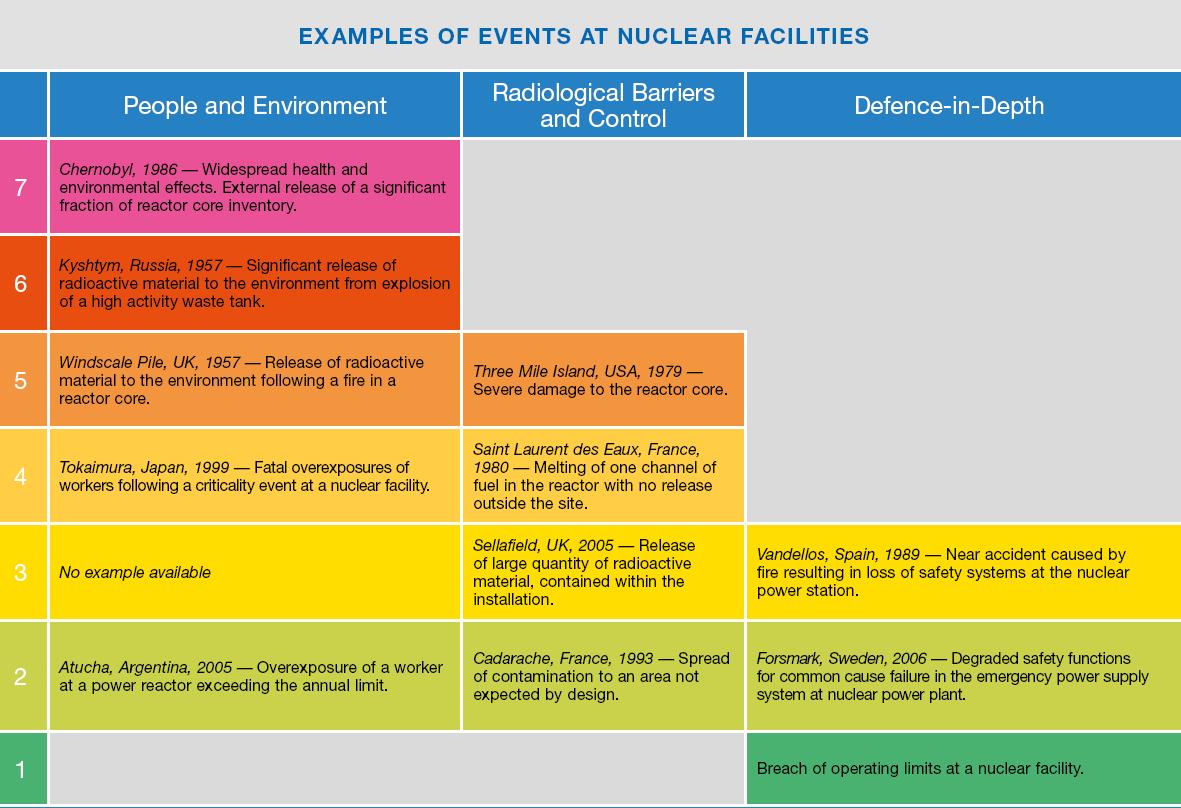
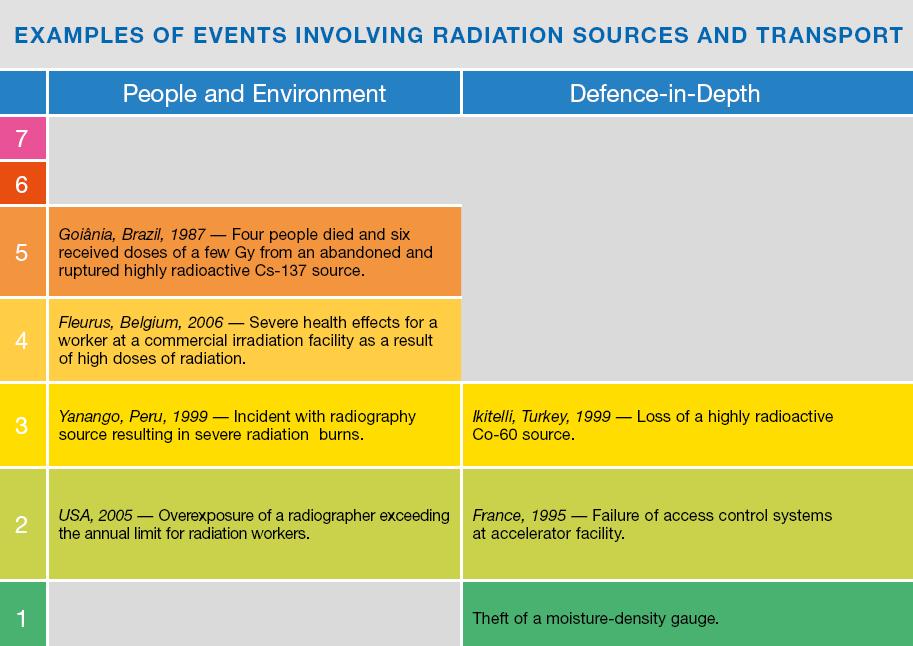
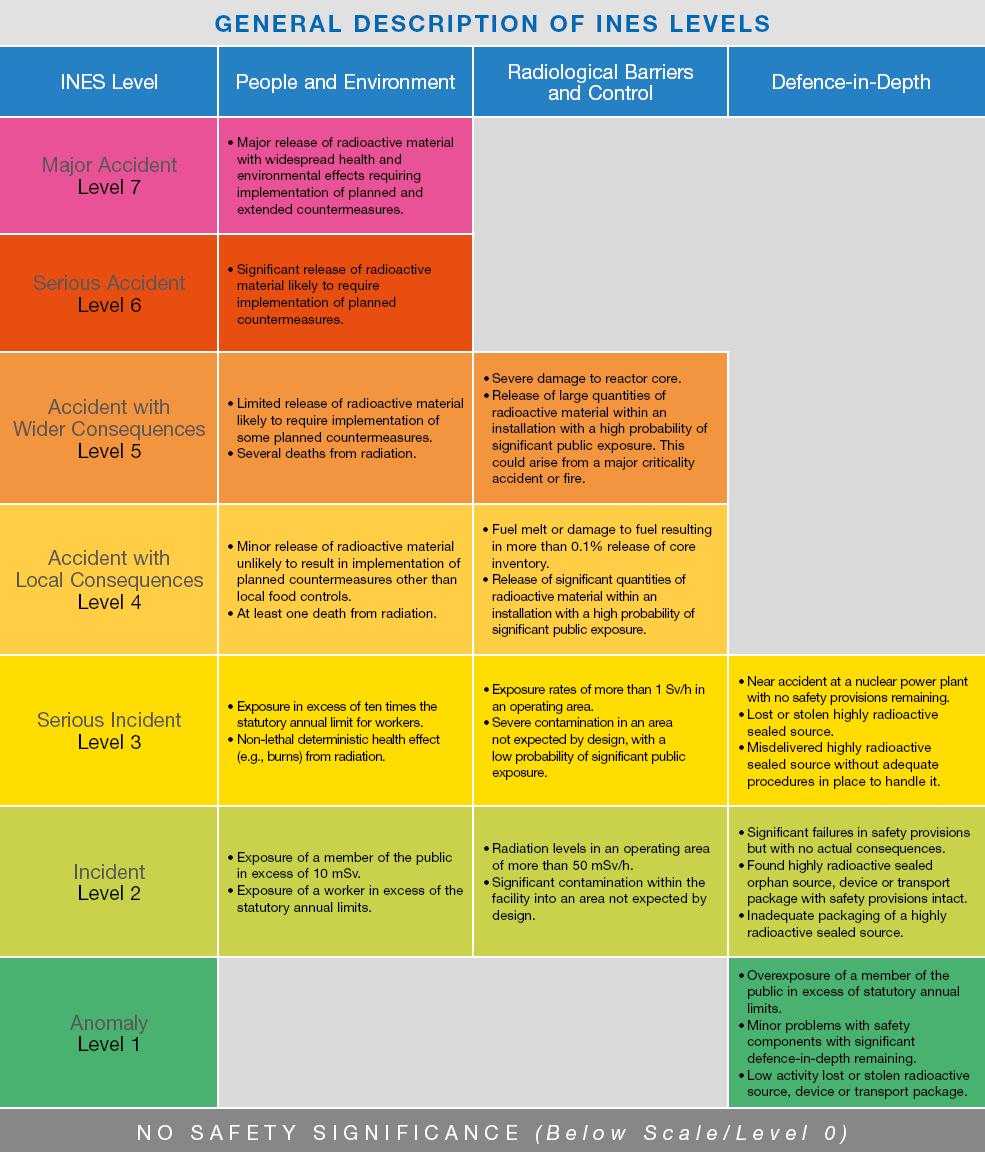
Events are classified on the scale at seven levels: Levels 1?3 are called "incidents" and Levels 4?7 "accidents". The scale is designed so that the severity of an event is about ten times greater for each increase in level on the scale. Events without safety significance are called “deviations” and are classified Below Scale / Level 0.
INES classifies nuclear and radiological accidents and incidents by considering three areas of impact:
People and the Environment
covers the radiation doses to people close to the location of the event and the widespread, unplanned release of radioactive material from an installation.
Radiological Barriers and Control
covers events without any direct impact on people or the environment and only applies inside major facilities. It covers unplanned high radiation levels and the spread of significant quantities of radioactive materials confined within the installation.
Defence-in-Depth
also covers events without any direct impact on people or the environment, but for which the range of measures put in place to prevent accidents did not function as intended.
Communicating Information about Incidents and Accidents
Nuclear and radiological events are promptly communicated by the INES Member States to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). In some situations, where not all the details of the event are known early on, a provisional rating may be issued. Later, a final rating is determined and any differences explained.
To facilitate international communications for events attracting wider interest, the IAEA maintains a web-based communications network that allows details of the event to immediately be made publicly available.
Since 1990 the scale has been applied to classify events at nuclear power plants, but it has subsequently been extended to enable it to be applied to all installations associated with the civil nuclear industry. By 2006, it had been adapted to meet the growing need for communication of the significance of all events associated with the transport, storage and use of radioactive material and radiation sources.
The IAEA has coordinated its development in cooperation with the OECD/NEA and with the support of more than 60 Member States through their officially designated INES National Officers.